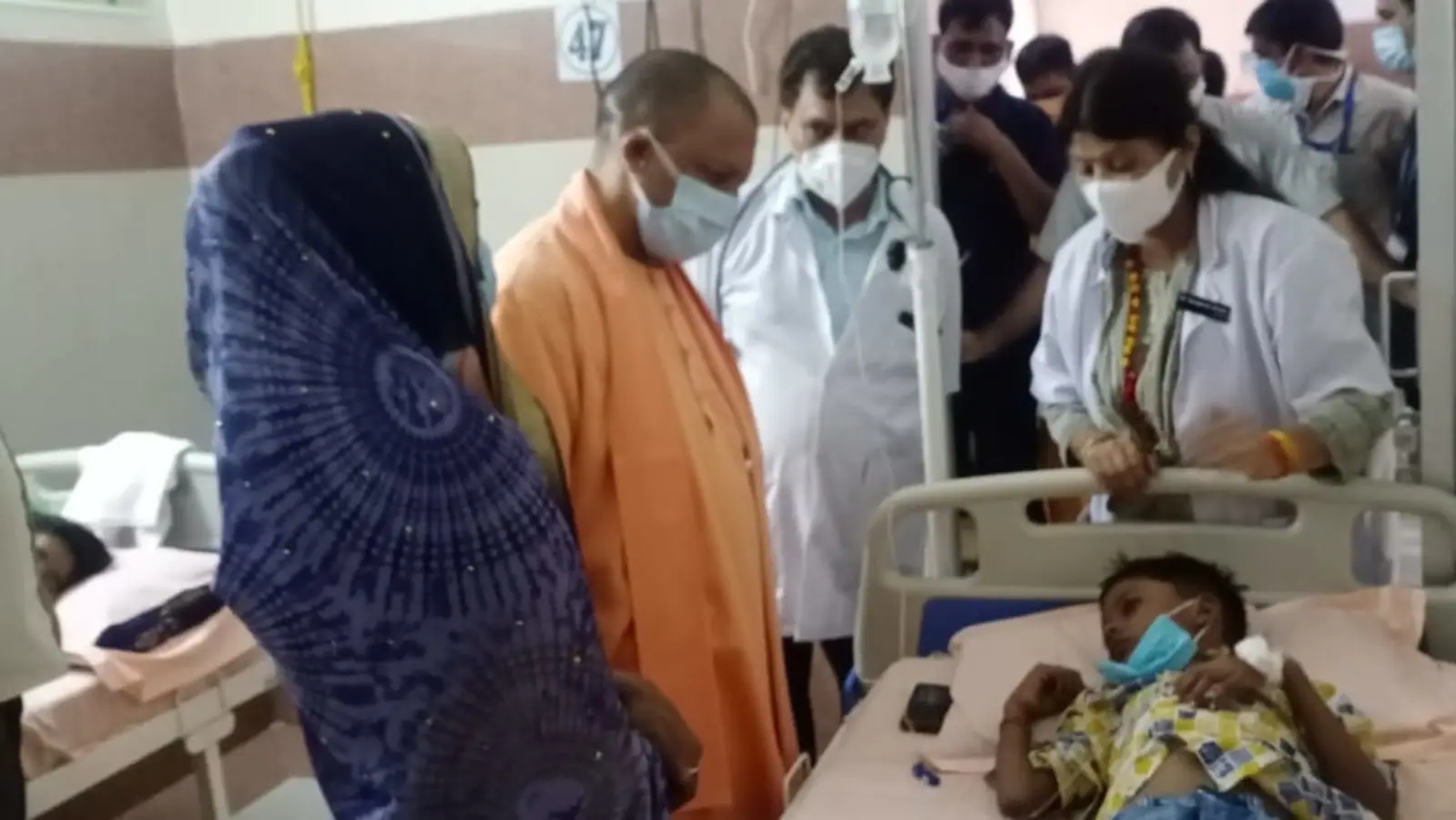
In the summer of 2023, Uttar Pradesh (UP) found itself grappling with a relentless and rapidly spreading enemy – dengue fever. The state, known for its rich cultural heritage and diverse landscape, has recently been thrust into the spotlight for an alarming rise in dengue cases. This article explores the dengue outbreak in UP in 2023, shedding light on its causes, consequences, and the measures taken to combat it.
Understanding Dengue Fever
Dengue fever, caused by the dengue virus, is a mosquito-borne disease that presents with symptoms ranging from mild fever to severe hemorrhagic fever. It is transmitted primarily by the Aedes mosquito, particularly Aedes aegypti. Dengue has been a significant public health concern in tropical and subtropical regions for decades.
The dengue virus has four distinct serotypes (DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3, and DEN-4). Once infected with one serotype, individuals develop immunity to that specific serotype but remain susceptible to infection by the other three. Multiple infections with different serotypes can increase the risk of severe dengue, also known as dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome, which can be fatal.
Dengue in Uttar Pradesh: The 2023 Outbreak
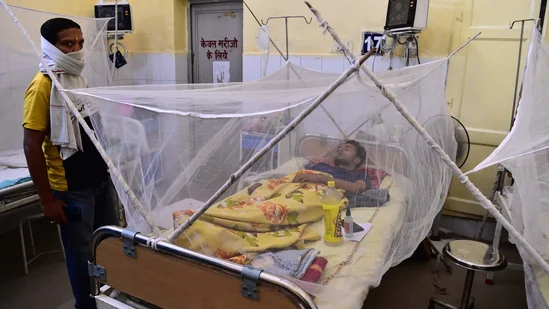
The dengue outbreak in Uttar Pradesh in 2023 has been particularly concerning. While the state has experienced sporadic outbreaks in the past, this year’s surge has raised alarm bells among health authorities, citizens, and policymakers alike.
1.Rising Case Numbers The number of reported dengue cases in UP has skyrocketed in 2023, far surpassing previous years. The state saw an exponential increase in cases from the onset of the monsoon season, and this surge showed no signs of abating.
2. **Geographical Spread**: Dengue has not been limited to a specific region within UP; it has affected both urban and rural areas. Cities like Lucknow, Kanpur, Varanasi, and Agra have witnessed a high incidence of cases, but the disease has also spread to remote villages.
3. **Overburdened Healthcare System**: The rapid increase in dengue cases has put immense pressure on UP’s healthcare infrastructure. Hospitals and clinics have been inundated with dengue patients, leading to overcrowding, strained resources, and a shortage of medical staff.
Beyond its toll on public health, the dengue outbreak has also had economic repercussions. Families have had to bear the financial burden of medical expenses, while businesses have suffered due to employee absenteeism and decreased productivity.
5. **Fear and Anxiety**: The fear of contracting dengue has gripped the population, leading to a decrease in outdoor activities, tourism, and social gatherings. People are apprehensive about sending their children to school, and many are taking precautions such as using mosquito nets and repellents.
Causes of the Dengue Outbreak
Several factors have contributed to the unprecedented dengue outbreak in Uttar Pradesh in 2023:
1. **Monsoon Rains**: Excessive monsoon rains created breeding grounds for Aedes mosquitoes, as they lay their eggs in stagnant water. The prolonged and heavy rainfall provided ample opportunities for mosquito larvae to thrive.
2. **Urbanization and Poor Waste Management**: Rapid urbanization in UP has led to inadequate waste management practices. Accumulated garbage and waterlogged areas in cities have become ideal breeding sites for mosquitoes.
3. **Climate Change**: Changing weather patterns and rising temperatures have expanded the geographical range of Aedes mosquitoes. They are now found in areas previously unaffected by dengue, increasing the vulnerability of the population.
4. **Lack of Awareness**: A lack of awareness about dengue prevention measures and symptoms has made it difficult for people to protect themselves adequately. Public education campaigns have often been insufficient.
Government Response
The Uttar Pradesh government has taken several steps to tackle the dengue outbreak:
1. **Mosquito Control Measures**: Intensive mosquito control measures, including fogging and the distribution of mosquito nets, have been initiated to reduce the mosquito population.
2. Healthcare Infrastructure**: The government has increased the capacity of hospitals and medical facilities to accommodate dengue patients. Specialized dengue treatment centers have been established in hotspots.
3. **Public Awareness Campaigns**: Public awareness campaigns have been launched to educate citizens about dengue symptoms, prevention methods, and the importance of seeking medical attention early.
4. **Collaboration with NGOs**: The government has collaborated with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) to mobilize resources and support for dengue prevention and control efforts.
5. **Community Engagement**: Local communities have been actively involved in clean-up drives to eliminate mosquito breeding sites and reduce the risk of dengue transmission.
1. **Overwhelmed Healthcare System**: The healthcare system in UP remains stretched, with hospitals struggling to cope with the influx of dengue patients.
2. **Mosquito Resistance**: Overreliance on insecticides for mosquito control has raised concerns about mosquito resistance, making control measures less effective.
3. **Climate Change**: Climate change continues to pose a long-term threat, potentially expanding the range of dengue-transmitting mosquitoes.
4. **Resource Constraints**: The state faces resource constraints in terms of funding, medical supplies, and trained healthcare personnel.
5. **Vaccine Development**: There is an urgent need for the development of a dengue vaccine that can provide long-term protection against all four serotypes of the virus.
Conclusion
The dengue outbreak in Uttar Pradesh in 2023 is a stark reminder of the public health challenges faced by the state. The rapid spread of the disease, overburdened healthcare system, and economic repercussions underscore the need for proactive measures to combat future outbreaks. It is imperative that the government, healthcare professionals, and communities work together to mitigate the impact of dengue and implement sustainable prevention strategies. Additionally, addressing the root causes, such as climate change and urbanization, will be crucial in preventing future outbreaks and safeguarding the health of UP’s population.